


Water Soluble Fertilizer
NPK 13:40:13
Arihant Group’s NPK 13:40:13 is a high-quality, water-soluble fertilizer designed…
Learn More


NPK 00:52:34
Arihant Group’s NPK 00:52:34 is a high-quality, water-soluble mono potassium…
Learn More
NPK 00:00:50
Arihant Group’s NPK 00:00:50 is a high-quality, water-soluble potassium sulfate…
Learn More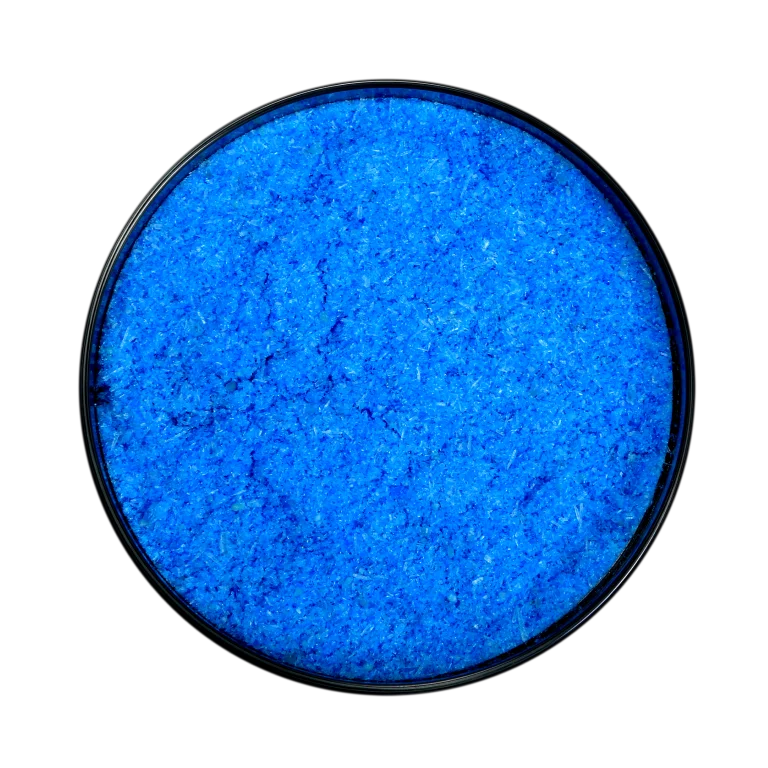
NPK 20-20-20 (Powder)
Arihant’s NPK 20-20-20 powder is a versatile fertilizer designed to…
Learn More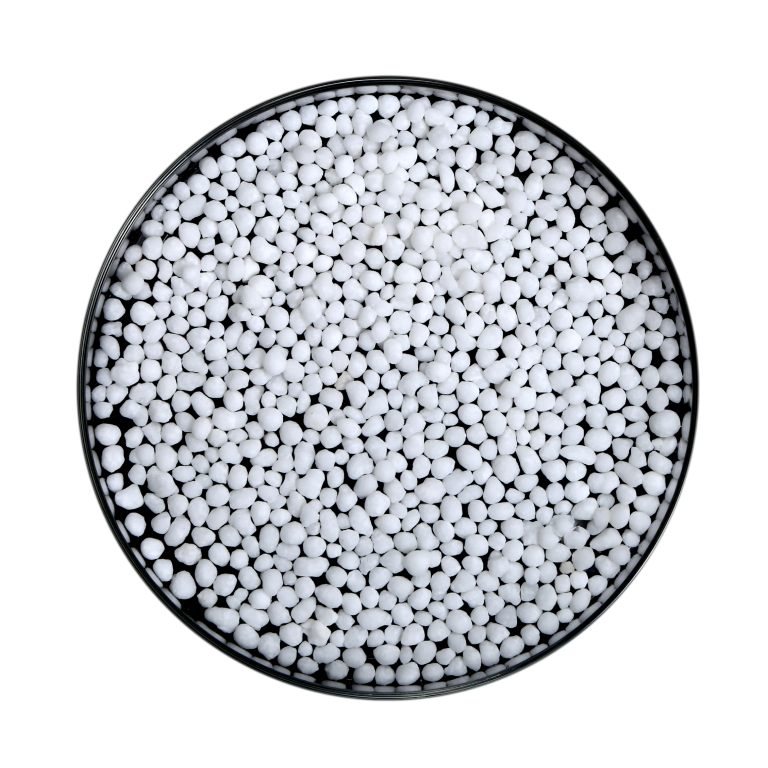
Calcium Nitrate Granule
Arihant Group’s Calcium Nitrate Granule is a premium, water-soluble fertilizer…
Learn More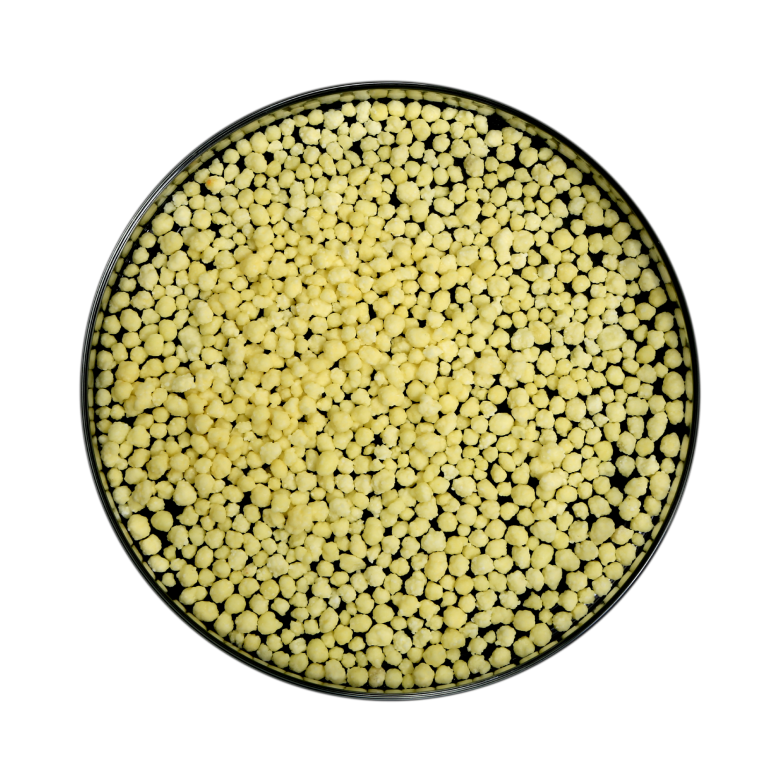
Boronated Calcium Nitrate Granule
Arihant Group’s Boronated Calcium Nitrate Granule is a top-quality, water-soluble…
Learn More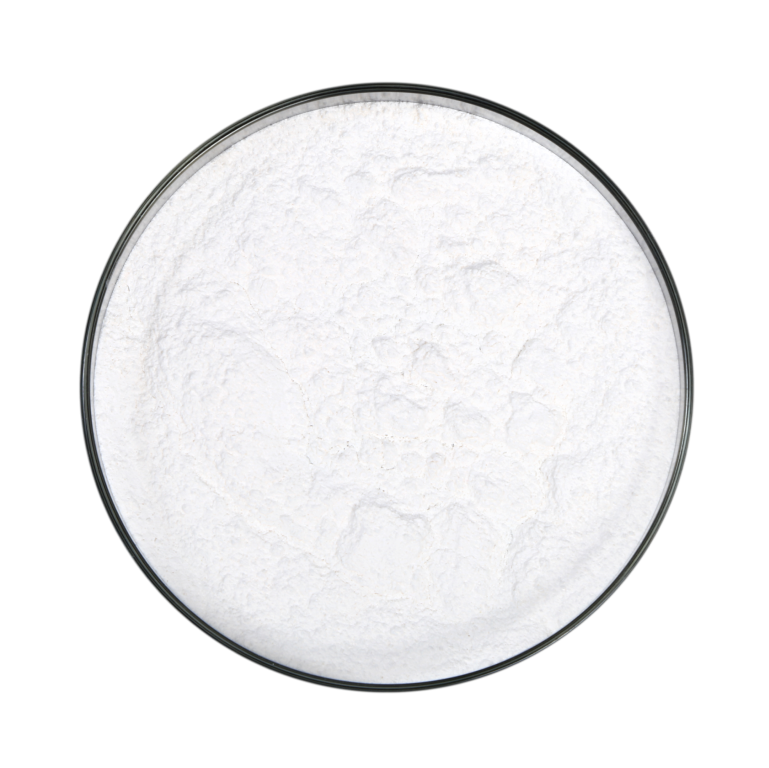
Potassium Schoenite
Arihant Group’s Potassium Schoenite is a high-quality, water-soluble fertilizer designed…
Learn More100 % WATER SOLUBLE FERTILIZER
Arihant Group’s water-dissolvable fertilizers are formulas that fully dissolve in water and are easily applied or washed out of the soil. Using these fertilizers, it becomes simple to manage the exact quantity of nutrients plants can absorb.
What is NPK and Why Does it Matter?
All greenery requires nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for development. A shortage of any one of these elements will cause the plant to fail.
Understanding the NPK values of a fertilizer helps you choose one that meets the specific needs of the plants you’re growing. For instance, if you’re cultivating leafy greens, you’ll likely want a fertilizer with a higher nitrogen value to promote leaf growth. Conversely, if you’re growing flowers, a fertilizer with a higher phosphorus content would be beneficial to encourage more blooms.
Before applying fertilizer to your garden or farm, it’s important to conduct a soil test. This allows you to determine the ideal fertilizer balance for your soil’s specific nutrient requirements and deficiencies.
Homogeneous NPKs – ARIHANT
The NPK fertilizers we offer are balanced to provide the right amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for your crop’s nutritional needs throughout its growing period. Additionally, we offer formulations enriched with secondary nutrients like magnesium and sulfur, along with micronutrients such as boron, iron, manganese, molybdenum, and zinc.
These homogeneous NPK fertilizers are designed to enhance both the yield and quality of your crops. Whether in prill or granule form, these products are perfect for high-value crops like vegetables, fruit trees, vines, and turf.
The benefit to the grower is the uniform nutrient distribution these fertilizers provide, whether spread by hand or machinery. There’s no risk of nutrient segregation during transport, handling, or application.
Efficient Nutrient Sources
Balanced Nitrogen Source – Nitrogen is available at 40-45% as nitrate-N and 55-60% as ammonium-N, depending on the production process and specific blend.
Fast Nitrogen Uptake – High nitrate-N content ensures a rapid response, while ammonium-N provides sustained nitrogen delivery.
Available Phosphate – Phosphorus is fully available to the plant in the form of water-soluble ortho- and polyphosphates and ammonium citrate soluble di-calcium phosphate. This combination ensures long-lasting phosphorus availability.
Alternative Potassium Sources– Potassium is included as either MOP (Muriate of Potash – potassium chloride) or SOP (Sulfate of Potash – potassium sulfate). SOP-based products are ideal for crops with low chloride tolerance, while MOP-based products suit all other crops.
Efficient fertilization methods and fertilizers have become the key to meeting the increasing demand for agricultural products. Modern farming must supply crops with the optimal nutrient ratios throughout their growth cycles in a way that preserves soil and water resources. Techniques like fertigation and foliar feeding allow for more efficient nutrient use.
Understanding NPK: Improving Your Soil
Your field requires nutrients just like your body needs food. Similar to how you track proteins, fats, and carbs, your plants need their own specific nutrient breakdown. This is where NPK—nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—comes in. While plant nutrients are naturally present in the soil, each plot can differ, and that’s why field products are often tailored to supply the perfect nutrient mix for what you’re growing.
What Does NPK Represent?
Just as our food consists of three main nutrients, your plants’ nutrients are similarly divided. Each of these nutrients plays a distinct role in supporting plant health.
N: Nitrogen

Within the proportion, N represents nitrogen. This naturally occurring element constitutes a significant portion of the air we inhale. However, the nitrogen in the atmosphere isn’t sufficient to nourish our plants, so we depend on organic materials and field products to supply adequate amounts of this nutrient from the roots upward. Nitrogen is essential for the development of leaves on a plant. In fact, you may be able to spot a nitrogen deficiency through yellowing leaves and thin stems. Nitrogen also aids plants in producing chlorophyll, a green pigment that enables the absorption of sunlight for photosynthesis. Green plants and vegetables generally require more nitrogen.
P: Phosphorus

Another essential nutrient for plant growth is potassium. It assists in transforming other nutrients into effective building blocks by promoting the development of a plant’s root system. Potassium primarily influences a plant’s ability to flower or bear fruit, earning it the nickname “flower booster.” As a result, a potassium deficiency might manifest when plants:
- Are smaller than expected
- Produce few (or no) flowers
- Have weak root systems
- Display a purple hue
Plants that bear fruit or produce flowers typically require higher levels of potassium, and the optimal time for applying potassium to the soil is in early spring, before blooms are expected. Potassium field products are available in both organic and synthetic forms. However, caution should be taken with synthetic potassium, as it may leach into the water supply and cause a significant salt buildup.
K: Potassium

Although it may seem counterintuitive, “K” is the symbol for potassium, which is the third macronutrient essential for plant health. Potassium supports overall plant function by strengthening cells to improve disease resistance, promote growth and resilience, and increase fruit production. While phosphorus drives the formation of blooms, potassium can help increase the size of those blooms—particularly useful when growing fruit. Potassium plays a key role in forest ecosystems as well, as wood ash from forest fires releases potassium and rejuvenates the soil. Providing potassium helps plants become more resilient against external factors, such as weather and pests. While detecting a potassium deficiency can be difficult, signs like yellowing leaf edges, downward curling leaves, and greater vulnerability to diseases may indicate a need for more potassium in the soil.
Types of Fertilizers
Every field, plant, and seed requires nutrients for growth. Fertilizers are crucial for delivering these nutrients and supporting the development of strong, healthy plants. With so many fertilizer options available, determining the best choice depends on the type of plant being fertilized and its specific stage of growth.


